中国科学院鄱阳湖湖泊湿地观测研究站(简称鄱阳湖站)位于江西省九江市星子县境内的鄱阳湖大湖区至湖口之间,是一个以鄱阳湖为典型研究对象,以湖泊与湿地生态系统及相互作用为观测研究内容的野外定位研究站。该站由中国科学院南京地理与湖泊研究所与江西省山江湖开发治理委员会办公室合作共建,总计征地2.4公顷。基础建设、实验设备以及观测试验设备累计投资1300多万元,其中获得科学院创新三期建设经费支持200万元,科学院野外观测研究站网络建设/维修专项经费80万元。2007年10月开工建设,2008年9月完成土建、生活区和实验室建设,2008年10月,中国科学院副院长丁仲礼为研究站揭牌,研究站正式投入运行。2012年3月28日,经过中国生态系统研究网络科学委员会会议投票表决,鄱阳湖站正式进入CERN。

丁仲礼副院长为鄱阳湖站揭牌
研究站目前有固定研究人员21人,支撑人员6人。拥有1800平方米的实验室、生活和会议用房,建有标准气象观测场,生物实验室、生态实验室、化学实验室、水文实验室、分析仪器室等,现有野外考察车一辆,野外采样和室内分析仪器42台套,能满足野外采样、样品处理及实验分析需要。目前研究站已在鄱阳湖流域布设水环境水生态长期定位观测点24个,湿地定位观测剖面4个,气象观测场1座,湿地水文观测综合站点1处,并已开展鄱阳湖湖泊水环境水生态及湖泊湿地连续的常规监测和调查研究工作。研究站拥有完善的生活设施及交通通讯设备,可以保证在站工作人员的信息交流畅通和优良的工作生活环境。
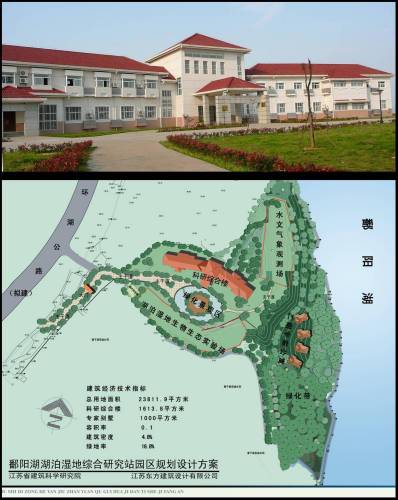
鄱阳湖站区规划及综合楼
人员介绍:
业务、行政负责人
研究站配备了站长一名,副站长2名。
陈宇炜:站长,全面负责站上科研、对外合作交流和管理;
张路:副站长,协助站长工作,负责监测、实验室管理,协助对外合作交流;
研究方向
围绕大型通江湖泊水安全与湿地生态保护领域关键科学问题,通过湖泊物理、化学和生物指标长期定位监测以及湖泊湿地典型剖面的水文生态过程和碳、氮、磷、硫等元素生物地球化学循环观测与控制试验,重点开展三个方面研究:
(1)湖泊水环境与水生态
研究鄱阳湖氮磷等污染物的迁移、转化、降解过程,赋存形态、时空分布特征及其与湖泊水文水动力条件变化的关系;开展湖泊富营养化发生主控生态与环境因子及对湖泊富营养化过程影响的原位监测和实验研究;探讨鄱阳湖浮游与底栖生物及沉水植被时空分布特征、浮游和底栖生物种群结构及优势类群变化对湖泊营养水平和水文水动力条件的响应机理,评估不同水情条件下湖泊蓝藻水华发生风险。
§ 湖泊营养盐迁移转化与水文水动力影响机制
§ 湖泊富营养化过程与机理
§ 湖泊生态系统结构、功能演替
(2)湿地水文生态过程与生物地球化学循环
研究不同水位梯度下湖泊洲滩湿地植被高程分布结构特征及水位周期性变化对湿地生物结构与生态类型的影响及自适应机理;基于典型湿地大气、水文、植被与土壤等关键水文生态要素及相互之间物质交换通量的定位观测,探讨不同湿地植被群落对污染物降解功能及湿地生态系统碳、氮、磷、硫等生源要素生物地球化学循环过程的影响。
§ 湿地分布格局与演替
§ 湿地水文生态过程
§ 湿地元素生物地球化学循环
(3)江河湖关系与湖泊水文水动力
研究不同水文年鄱阳湖流域五河入湖和长江来水不同水文情势组合条件下鄱阳湖与长江水沙营养盐交换关系以及鄱阳湖水位、水量及水动力场时空分布特征;分析评估长江三峡和流域五河大型水利工程建设对鄱阳湖水文水动力的影响方式与程度;研究鄱阳湖区干旱与洪水极端事件变化规律及其气候、三峡工程及湖泊演变等要素复合影响机制与调控途径,模拟鄱阳湖流域物质的产出与输移规律。
§ 江湖关系变化与机制
§ 湖泊水文水动力演变
§ 湖区干旱和洪水极端事件演变与调控
§ 湖泊流域物质产出与输移模拟
1.主要试验观测仪器
水化学实验室:主要包括便携式多参数水质分析仪(YSI,2套;Hydrolab,1套),可用于分析氮磷营养盐、碱度、阳离子、阴离子等水化学指标的化学间断分析仪,紫外可见分光光度计、灭菌锅、超纯水仪等化学分析仪器。
水生生物实验室:配备有荧光倒置显微镜、解剖镜、超净工作台、光照培养箱、生化培养箱、显微计数器等。
水文湿地实验室:配备有流速仪,水位仪、土壤含水率仪、光合作用仪、土壤pH计、土壤电导率仪、湿地植物叶片分析、湿地温室气体培养箱等。
气象观测仪器:包括维萨拉自动气象观测站、满足国家气象观测规范和CERN规范的人工气象观测仪器。主要为:气象观测避雷系统一套;维萨拉自动风速风向仪、太阳辐射仪、气温、湿度系统一套;EL-电结风向风速仪一套;毛发湿度计一套;口径30厘米蒸发皿一个、E601蒸发器一个;翻斗式自记雨量计一套;百叶箱两个(装有高低温度计、气压计等监测仪器);地温观测仪器一套等。



鄱阳湖站实验室
学术论文
2008年鄱阳湖站成立后至2013年间,围绕鄱阳湖水环境变化、生态演变、湿地与水位、湿地群落及物质循环、江湖作用关系、气候与水文等方面研究,共发表论文100多篇,其中SCI/EI论文57篇(TOP SCI 5篇),出版专著4部,获得软件著作权登记5项。
SCI/EI论文57篇:
1. Hua Guo, Qi Hu, Qi Zhang, Song Feng. 2012. Effects of the Three Gorges Dam on Yangtze River flow and river interaction with Poyang Lake, China: 2003–2008. Journal of Hydrology, 416–417, 19–27. (TOP-SCI)
2. Liu Y, T Hiyama, Y Yasunari, H Tanaka. 2012. A nonparametric approach to estimating terrestrial evaporation: validation in eddy covariance sites. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 152:49-59. DOI:10.1016/j.agrformet.2012.01.012 (TOP-SCI)
3. Xiang-Hu Li, Qi Zhang, Chong-Yu Xu. 2012. Suitability of the TRMM satellite rainfalls in driving a distributed hydrological model for water balance computations in Xinjiang catchment, Poyang lake basin. Journal of Hydrology, 426–427, 28–38. (TOP-SCI)
4. Lai X., Monnier J. Assimilation of spatially distributed water levels into a shallow-water flood model, Part I: mathematical method and test case. Journal of Hydrology. 2009, 377(1-2):1-11. (TOP-SCI)
5. Hui Tao, Marco Gemmer, Jiahu Jiang, Xijun Lai & Zengxin Zhang. Assessment of CMIP3 climate models and projected changes of precipitation and temperature in the Yangtze River Basin,China Climatic Change,2011(TOP-SCI)
6. Caihong Liu, Ligang Xu, Haiying Gao.Water quality evaluation in representative lake based on principal component analysis. Proceeding of RSETE, 2011, v4, p 4704-4707. (EI)
7. Gu Yajin, Wang Hongli, Liu Jian. 2010. Latitudinal-dependent Response of East Asian Summer Monsoon to External Forcing in the Last Millennium. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 24(6), 671-679
8. Hui Tao a, Marco Gemmer b, Yungang Bai , Buda Su , Weiyi Mao. Trends of streamflow in the Tarim River Basin during the past 50 years: Human impact or climate change? Journal of Hydrology. 400 (2011) 1–9
9. Jian Peng, Yuanbo Liu. Estimation of evaporative fraction from top-of-atmosphere radiance. IAHS Red Book,2011, 343, 47-52
10. Jiang Jiahu, Lai Xijun, Huang Qun. The characteristics of flood responses to the restoration of polders on Dongting Lake, China. Hydrological Sciences Journal,2007,52(4):671-685.
11. Jin Xu, Ligang Xu, Jinbao Wan, Shu Li. Phosphorus retention and release by constucted wetland soils. Proceeding of ISWREP, 2011, 1799-1802.
12. Lai X, Li J, Yesou H., Flow dynamic modeling of the monsoon lake (The Poyang Lake). European Space Agency SP , 2010,684SP
13. Li Xianghu, Qi Zhang, Liliang Ren. Assessment of downscaling evapotranspiration estimates using Shuttleworth-Wallace model and monthly meteorological data for daily streamflow simulation. IAHS Publication 2011, 350: 188-193.
14. Li Xianghu, Ren Liliang, Wang Guizuo. Improvement of the distributed hydrological AFFDEF model for runoff simulation. IAHS Publ. 335, 2009, 33-41.
15. Li Xianghu, Zhang Qi, Li Yunliang, Shao Min. Interannual variability of evapotranspiration based on distributed hydrological model in Xinjiang catchment, Poyang Lake. Proceeding of ISWREP, 2011, v1, p 580-583.
16. Li Xianghu, Zhang Qi, Li Yunliang. Comparison of two distributed hydrological model for soil moisture simulation. Proceeding of RSETE, 2011, v4, p 3018-3021.
17. Li Xianghu, Zhang Qi, Li Yunliang. Validation the applicability of satellite based rainfall data for runoff simulation and water balance analysis. Proceeding of ISWREP, 2011, v1, p 494-496.
18. Li Xianghu, Zhang Qi. Estimating the Potential Evapotranspiration of Poyang Lake Basin Using Remote Sense Data and Shuttleworth-Wallace Model. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2011, 10: 1575-1582.
19. Li Xianghu, Zhang Qi. Validation of satellite based rainfall data in Poyang Lake catchment. Proceeding of RSETE, 2011, v4, p 3756-3759.
20. Li, X., Zhang, Q., Li, Y., Shao, M., 2011. Interannual variability of evapotranspiration based on distributed hydrological model in Xinjiang catchment, Poyang Lake. IEEE, pp. 580-583.
21. Ligang Xu, Jiahu Jiang, Jinbao Wan, Jin Xu, Shu Li, Ping Gu. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Water Pollution and Water Quality Evaluation in Poyang Lake. Proceeding of ISWREP, 2011, v1, 794-797.
22. Ligang Xu, Jingsong Yang, Qi Zhang, Hailin Niu. Modelling water and salt transport in a soil-water-plant system under different groundwater tables. Water and Environment Journal, 2008, 22,265-273.
23. Ligang Xu, Qi Zhang, Lijiang Huang Nitrogen leaching in a typical agricultural extensively cropped catchment, China: experiments and modelling Water and Environmental Journal, 2010, 24(2): 97-106
24. Liu Y, P Song, J Peng, C Ye. 2012. A physical explanation of the variation in threshold for delineating terrestrial water surface from multi-temporal images: effects of radiometric correction. International Journal of Remote Sensing. DOI:10.1080/01431161.2012.675452.
25. Liu Y, Y Noumi, Y Yamaguchi. 2011. Quantifying variability of satellite data in the reflective band for long-term monitoring of the Earth's surface: inference from a multi-temporal relationship between remotely sensed pixels. International Journal of Remote Sensing 32:7717-7730. DOI:10.1080/01431161.2010.527394
26. Liu, Y., Song, P., Peng, J., Fu, Q., Dou, C., 2011. Recent increased frequency of drought events in Poyang Lake Basin, China: climate change or anthropogenic effects? IAHS-AISH publication, 99-104.
27. Masaki Hayashi, John Jackson, and Ligang Xu. Application of the Versatile Soil Moisture Budget model to estimate evaporation from prairie grassland. Canadian Water Resources Journal, 2010, 35(2): 187-208.
28. Peng Jian, Yuanbo Liu, Xiaosong Zhao, et al A Novel Approach to Calculating Water Stress Index Image and Signal Processing (CISP), 2010 3rd International Congress on, 2010, 16-18: 2085-2088
29. Peng, J., Liu, Y., 2011. Estimation of evaporative fraction from top-of-atmosphere radiance. IAHS-AISH publication, 47-52.
30. Ping Song, Yuanbo Liu. Satellite-based Tracking of Water Surface Variation of Poyang Lake in Recent Three Decades . IAHS Red Book, 2011,344, 215-220
31. Qi Zhang, Adrian Werner. Integrated surface-subsurface modeling of Fuxianhu Lake catchment, Southwest China. Water Resources management, 2009, 23: 2189-2204.
32. Qi Zhang, Lijiao Li. Development and application of an integrated surface runoff and groundwater flow model for a catchment of Lake Taihu watershed, China. Quaternary International, 2009, 208(1-2): 102-108.
33. Song P, Liu Y, Zhao D, Ye C, Peng J. 2010. Temporal influences on thresholding for satellite retrival of water surface areas. IEEE The 6th International Conference on Wireless Communications Networking and Mobile Computing (WiCOM): 1-4. DOI:10.1109/WICOM.5601045.
34. Wang Xiaolong, Han Jingyi, Xu Ligang, et al Effects of anthropogenic activities on chemical contamination within the Grand Canal, China Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2011, 177(1-4): 127-139
35. X. B. CHEN, L. G. XU, Z. G. Sun, J.B. YU & J. H. JIANG. Hydro-salinity balance and mobilisation in oasis irrigation areas at two different scales. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2011, 62: 161-169.
36. Xiaodong Wu, Fanxiang Kong,Yuwei Chen, Xin Qian, Longjiang Zhang, Yang Yu, Min Zhang and Peng Xing Horizontal distribution and transport processes of bloom-forming Microcystis in a large shallow lake (Taihu, China) Limnology, 2010, 40(1): 8-15
37. Xiaolan Song, Zhengwen Liu, Guijun Yang and Yuwei Chen Effects of resuspension and eutrophication level on summer phytoplankton dynamics in two hypertrophic areas of Lake Taihu, China Aquatic Ecology, 2010, 44(1): 41-54
38. Xiaoli Jin, Chong-yu Xu, Qi Zhang, Yongqin David Chen. Regionalization study of a conceptual hydrological model in Dongjiang Basin, south China. Quaternary International, 2009. 208, 129-137.
39. Xiaoli Jin, Chong-yu Xu, Qi Zhang, Yongqin David Chen. Regionalization study of a conceptual hydrological model in Dongjiang Basin, south China. Quaternary International, 2009. 208, 129-137.
40. Xiaolong Wang, Jingyi Han, Ligang Xu, et al Spatial and seasonal variations of the contamination within water body of the Grand Canal, China Environmental Pollution, 2010, 158(5):1513–1520
41. Xuchun Ye, Qi Zhang, Li Bai, Qi Hu. 2011. A modeling study of catchment discharge to the Poyang Lake under future climate in China. Quaternary International, 244(2): 221-229.
42. Xue Lijuan, Li Lijiao, Zhang Qi. Hydrological behaviour and water balance analysis for Xitiaoxi catchment of Taihu Basin. Water Science and Engineering, 2008, 1(3), 45-54.
43. Ye C, Liu Y, Peng J, Song P, Zhao D. 2010. Improving MODIS land cover classification using NDVI time-series and support vector machine in the Poyang Lake Basin, China. IEEE The 6th International conference on Wireless Communications networking and Mobile Computing (WiCOM):1-4.DOI: 10.1109/WICOM.5601047.
44. Ye Xuchun, Zhang Qi and Viney N R The effect of soil data resolution on hydrological processes modelling in a large humid watershed Hydrological Processes, 2010, 25(1): 130-140
45. Ye Xuchun, Zhang Qi, Bai Li A modelling study of catchment discharge to Poyang Lake under future climate in China Quaternary International, 2010 DOI:101016/jquaint201007004
46. Ye, X., Liu, J., Zhang, Q., 2011a. A modeling study of hydrological response to landuse changes based on hypothetical scenarios for the Poyang Lake catchment. IEEE, pp. 550-553.
47. Yésou Hervé, Huber Claire, Lai Xijun, Averty Stéphane, Li Jiren, Daillet Sylviane, Bergé-Nguyen Muriel, Chen Xiaoling, Huang Shifeng, James Burnham, Crétaux Jean-François, Marie Tiphanie, Li Jinggang, Andreoli Rémi, and Uribe Carlos. Nine years of water resources monitoring over the middle reaches of the Yangtze River, with ENVISAT, MODIS, Beijing-1 time series, Altimetric data and field measurements. Lakes & Reservoirs: Research & Management, Special Issue: WLC Special Issue, 2011, 16(3): 231–247.
48. Yuanbo Liu, Ping Song, Jian Peng, Qiaoni Fu, Cuicui Dou. Recent increased frequency of drought events in Poyang Lake Basin, China: climate change or anthropogenic effects? IAHS Red Book, 2011,344, 99-104
49. Yuanbo Liu, Yousuke Noumi & Yasushi Yamaguchi. Quantifying variability of satellite data in the reflective band for long-term monitoring of the Earth's surface: inference from a multi-temporal relationship between remotely sensed pixels. International Journal of Remote Sensing.2011,32,7717-7730
50. Zhang Qi, Adrian D. Werner, Raden F. Aviyanto, John L. Hutson. Influence of soil moisture hysteresis on the functioning of capillary barriers. Hydrological Processes. 2009, 23, 1369–1375.
51. Zhang Qi, Yang Jinling. Improvement of modelling accuracy by using high resolution soil data in a coupled surface-subsurface water flow model. 2011 World Congress on Engineering and Technology, ISBN: 978-1-61284-363-6, 2011, p 449-452.
52. Zhang Qi. Development and Application of an Integrated Hydrological Model for Lake Watersheds. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2011, 10: 1630 -1636.
53. Zhang Qi. Sensitivity Assessment for Soil Hydraulic Conductivity in a Coupled Surface-Subsurface Water Flow Model. International Conference on Water Resources Management and Engineering, 2011, 75-78.
54. Zhang, Q., Viney, N.R., 2008. Development and testing of a distributed hydrological model with comparison to a conceptual lumped model. Proceedings of Water Down Under 2008, incorporating 31st Hydrology and Water Resources Symposium and 4th International Conference on Water Resources and Environment Research, 14-17 April 2008, Adelaide, Australia, 1319-1329. ISBN 0858257351, Engineers Australia, 2008.
55. Zhao Xiaosong, Yuanbo Liu, Tanaka Hiroki, et al A comparison of flux variance and surface renewal methods with eddy covariance IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2010, 3(3): 345-350
56. Zhonghua ZHAO, Lu ZHANG*, Jinglu WU,Miao JIN,and Chengxin FAN. Evaluation of Dispersive Liquid–liquid Microextraction Coupled with Gas Chromatography-microelectron Capture Detection (GC-μECD) for the Determination of Organochlorine Pesticides in Water Sample. ANALYTICAL SCIENCES. 2011,27(5):547-553
57. Zuo Haijun, Zhang Qi, Ma Luyi, Hartmann Heike, Zhai Jianqing, Xu Ligang. Evaluation of soil water percolation in response to different rainfall conditions using HYDRUS-1D model in the low hill red soil region of Jiangxi, China. Research journal of soil and water management. 2010, 1(3-4): 76-84.
CSCD论文46篇:
1.白丽, 张奇, 李相虎. 湖泊水量变化影响因子研究综述 水电能源科学, 2010, 28(3): 30-36
2.崔锐, 吕伟明, 刘广明, 高红霞, 徐力刚. 重金属污染土壤的螯合诱导植物修复技术研究进展,农业环境与发展,2009,26(2): 69-73.
3.豆翠翠, 刘元波, 阮仁宗. 2012. 不同时相MODIS L1B产品数据之间定量关系研究. 遥感学报. 16(4).(印刷中)
4.高海鹰, 黄丽江,张奇,徐力刚. 不同降雨强度对农田土壤氮素淋失的影响及LEACHM模型验证. 农业环境科学学报, 2008, 27(4), 1346-1352.
5.高海鹰, 张奇, 庄霞. 土壤水下渗解析解与数值解比较研究. 水土保持通报, 2010, 30(6): 1-6.
6.郭华 张奇, 2011. 近50年来长江与鄱阳湖水文相互作用的变化.地理学报 66(5):609-618
7.姜加虎,黄群.洞庭湖淤积、围垦对湖区江湖洪水影响的模拟.长江流域资源与环境,2006,15(5):584-587.
8.靳晓莉, 张奇, 许崇育. 一个概念性水文模型的参数区域化研究: 以东江流域为例. 湖泊科学,2008,20(6),723-732.
9.赖锡军 姜加虎 黄群 徐力刚. 鄱阳湖二维水动力和水质耦合数值模拟. 湖泊科学, 2011, 23(6):893-902
10.赖锡军, 傅 国圣, 孙波. 非恒定水流计算的最优控制问题及其变分求解. 水科学进展, 2008,19(4): 537-545
11.赖锡军, 姜 加虎, 黄群. 应用最优控制理论自动率定二维浅水方程的糙率参数. 水科学进展, 2008,19(3): 383-388
12.赖锡军. 洪 水淹没范围数据与动力学模型的融合.河海大学学报 (自然科学版), 2009, 37(5): 529-533
13.赖锡军.水 动力学模型与集合卡尔曼滤波耦合的实时校正多变量分析方法[J].水科学进展,2009,20(2):241-248
14.李相虎, 任立良, 张奇等 蒸散发时间尺度转换在日降雨径流过程模拟中的应用 湖泊科学, 2010, 22(5): 749-756
15.刘健, 张奇, 许崇育, 张增信. 近50年鄱阳湖流域径流变化特征研究. 热带地理. 2009,29(3),213-218,224.
16.刘健, 张奇, 左海军, 靳晓莉, 李丽娇, 叶许春. 鄱阳湖流域径流模型. 湖泊科学. 2009, 21(4): 570-578.
17.刘健,张奇. 一个新的分布式水文模型在鄱阳湖赣江流域的验证. 长江流域资源与环境, 2009, 18(1), 20-27.
18.刘元波, 傅巧妮, 宋平, 赵晓松, 豆翠翠, 2011. 卫星遥感反演降水研究综述. 地球科学进展 26, 1162-1172.
19.刘苑,陈宇炜,邓建明 YSI(多参数水质检测仪)测定叶绿素a浓度的准确性及误差探讨 湖泊科学, 2010, 22(6): 965-968
20.闵屾, 刘健, 2011. 鄱阳湖区域极端降水异常的特征及成因. 湖泊科学 23, 435-444.
21.钱子俊, 高海鹰, 王晓龙. 淡水湖泊河口区磷的输入迁移及其对藻类生长的影响.土 壤, 2011, 43 (5): 681~687
22.商景阁, 张路, 张波等. 中国长足摇蚊(Tanypus chinensis) 幼虫底栖扰动对沉积物溶解氧特征及反硝化的影响 湖泊科学, 2010, 22(5): 708-713
23.宋平, 刘元波, 刘燕春. 2011. 陆地水体参数的卫星遥感反演研究进展. 地球科学进展 26, 731-740.
24.孙占东,黄群,Opp Christian. 经验正交函数分解方法对降水模式与极端水文过程的研究. 长江流域资源与环境,2012,(3):.
25.汪迎春 赖锡军 姜加虎 黄群. 三峡水库调节典型时段对鄱阳湖湿地水情特征的影响. 湖 泊科学, 2011,23(2):191-195
26.王晓龙,徐力刚, 姚鑫等 鄱阳湖典型湿地植被土壤微生物量特征研究 生态学报, 2010 30(18): 5033-5042
27.王晓龙,徐力刚,白丽,张奇. 鄱阳湖典型湿地植物群落土壤酶活性. 生态学杂志2011,30(4): 798-803
28.徐进, 徐力刚, 张奇. 磷素在湖滨湿地基质-上覆水界面中的迁移过程. 湖泊科学. 2009, 21(5): 675-681.
29.徐进, 张奇, 徐力刚. 三级串联湿地对氮磷的净化效果. 生态环境学报,2009,l8(1):79-82.
30.徐进,张奇,徐力刚. 湿地基质-水界面中磷的迁移特征. 安徽农业科学,2009,37(24):11675-11677.
31.徐力刚, 叶昌, 张奇, 姜加虎, 高海鹰. 基于模糊模式识别的地下水水质综合评价研究.水文地质与工程地质, 2011, 38(5): 7-12.
32.徐力刚, 张奇, 徐进, 蒋鸿昆, 黄丽江. 不同降雨强度对营养盐垂向迁移过程和淋失量的影响. 土壤学报, 2008,45(3),437-444.
33.徐力刚, 张奇, 左海军. 地表水地下水的交互与耦合模拟研究现状与进展. 水资源保护, 2009, 29(5): 82-85.
34.徐怡波, 赖锡军, 周春国. 基于卫星雷达数据的鄱阳湖湿地水面检测与淹露分析 中国环境科学, 2010, 30(S1): 57-63
35.杨莹,刘元波,阮仁宗,叶春,卢盼盼. 2012. MODIS土地覆盖分类的尺度不确定性研究. 遥感学报. 16(4).(印刷中)
36.叶许春, 张奇. 网格大小选择对分布式水文模型水文过程模拟的影响 水土保持通报, 2010, 30(3): 112-116
37.叶许春,张奇,刘健,李丽娇,郭华. 气候变化和人类活动对鄱阳湖流域径流变化的影响研究. 冰川冻土. 2009,31(5),835-842.
38.叶许春,张奇,刘健,徐力刚. 2012. 鄱阳湖流域天然径流变化特征与水旱灾害. 自然灾害学报, 21(1), 9-16.
39.叶许春,张奇,刘健等. 土壤空间分辨率对水文过程模拟的影响. 地理科学进展,2009,28(4): 503-511.
40.余莉, 何隆华, 张 奇, 陈宇炜, 王晓龙. 三峡工程蓄水运行对鄱阳湖典型湿地植被的影响.地理研究, 2011,30 (1): 134-144
41.俞云利, 赖 锡军. 二维平面非恒定流数学模型的遥感水位数据同化. 水科学进展, 2008,19(2): 224-231
42.左海军, 张奇, 马履一等. 不同种植方式下农田渗漏水硝态氮含量的动态变化特征研究 水土保持学报, 2010, 24(5): 174-179
43.左海军,张奇,徐力刚,李丽娇,叶许春.农田土壤氮素径流损失的影响因素及其防治措施研究.灌溉排水学报.2009,28(6).
44.左海军,张奇,徐力刚,刘健,王晓龙.基于数值模拟的土壤水渗漏对降雨条件的响应研究.水土保持学报.2009,23(1):31-35;
45.左海军,张奇,徐力刚,王晓龙,吴忠东,吕伟明.集约化种植条件下土壤硝态氮动态变化及累积特征研究.水土保持通报.2009,29(4):214-219.
46.左海军,张奇,徐力刚. 农田氮素淋溶损失影响因素及防治对策研究。环境污染与防治, 2008, 30(12),83-89.
专著和译著:4部
1. 周文斌, 万金保, 姜加虎.2011. 鄱阳湖江湖水位变化对其生态系统影响.北京:科学出版社.
2. 姜加虎, 窦鸿身, 苏守德.2009. 江淮中下游淡水湖群. 武汉:长江出版社.
3. 刘元波,张奇,刘健,李恒鹏. 2012.《鄱阳湖流域气候水文变化及水环境效应》,科学出版社。
4. 刘元波. 2011.《水文气候学:视角与应用》, 高等教育出版社。
软件著作权登记和专利 5项 :
1. 徐力刚. 土壤地下水补给量模拟系统. 中华人民共和国国家版权局计算机软件著作权登记证书. (证书号:2010SR021778)
2. 徐力刚. 土壤水盐运移数值模拟系统. 中华人民共和国国家版权局计算机软件著作权登记证书. (证书号:2010SR021752)
3. 张奇. 湖泊集水域水文模拟软件. 中华人民共和国国家版权局计算机软件著作权登记证书. (证书号:2009SR045430)
4. 张奇, 刘波, 翟松. 实用新型名称: 一种陆面蒸散发过程观测系统. 中华人民共和国国家知识产权局, 专利号: ZL 2009 2 0170684.4
5. 赖锡军. 二维非结构网格流体计算软件. 中华人民共和国国家版权局计算机软件著作权登记证书(登记号2010SR040596)
联系我们:
地址:江西省九江市星子县锦岗路113号,中科院鄱阳湖站
邮编:332899 电子邮件:ywchen@niglas.ac.cn luzhang@niglas.ac.cn
电话:0792-2677129 传真:0792-2677126
联系方式:沈宏 徐军 027-86780056 Email:wetland@ihb.ac.cn
地址:武汉市武昌区东湖南路7号
访问数量:

 当前位置:
当前位置:

